|
University of Nevada Las Vegas |
MEG426/626 Manufacturing Processes |
|
Department of Mechanical Engineering |
Fall Semester 2000 |
Metrology
Metrology
is the science of measurement.Measurement
is a procedure in which an unknown quantity is compared to a known standard using an accepted and consistent system of units.Inspection
: is a procedure in which a part or product characteristic, such as a dimension, is examined to determine whether or not it conforms to the design specification.Accuracy
: is the degree to which the measured value agrees with the true value of the quantity of the interest.Precision
: is the degree of repeatability in the measurement process.Systematic errors
: are positive or negative deviations from the true value that are consistent from one measurement to the next (affect accuracy).Random errors
: are usually associated with human participation in the measurement process (affect precision).Mean
(m ) is a measure of the central tendency in the distribution (the average). 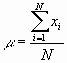
where N = number of members in the population; xi = variable of interest.
Standard deviation
(s ) is a measure of spread or scatter in the population expressed in the original units. 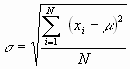
± 3s of the population = 99.7% (for normal distribution).
Rules for choosing measuring instrument
:
![]()
Created by Dr. Wang