Lattice Constants
Axial Length
Interaxial Angle
a
a
b
b
c
g
|
|
University of Nevada Las Vegas |
|
MEG301 Structures and Properties of Solids |
|
|
Department of Mechanical Engineering |
|
Fall Semester 2000 |
Crystal Structures
Crystal
: a solid composed of atoms, ions, or molecules arranged in a pattern that is repeated in three dimensions. Examples: metals, alloys, and some ceramic materials.Crystal Structure
: a regular three-dimensional pattern of atoms or ions in space.Space Lattice:
a three-dimensional array of points each of which has identical surroundingsLattice Point:
one point in an array in which all the points have identical surroundings.Unit Cell:
the smallest repetitive pattern (or atomic order) in a crystalline solid.Lattice Constants:
the size and shape of a unit cell can be described by three lattice vectors a, b, and c, originating from one corner of the unit cell. The axial lengths, a, b, and c and the interaxial angles a , b , and g are the lattice constants.
|
Lattice Constants |
Axial Length |
Interaxial Angle |
|
|
a |
a |
|
b |
b |
|
|
c |
g |
Bravais Lattices:
|
Crystal System |
Space Lattice |
Axial length and Interaxial Angle |
|
|
Cubic |
Simple cubic
|
|
a = b = c,a = b = g = 900 |
|
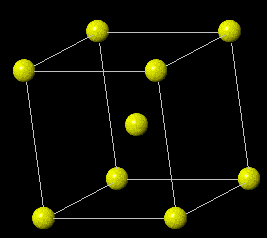
Body-centered cubic (BCC)
|
|
||
|
Face-centered cubic (FCC) |
|
||
|
Tetragonal |
Simple tetragonal
|
|
a = b ¹ c,a = b = g = 900 |
|
Body-centered tetragonal |
|||
|
Orthorhombic |
Simple orthorhombic |
|
a ¹ b ¹ c,a = b = g = 900 |
|
Body-centered orthorhombic |
|||
|
Face-centered orthorhombic |
|||
|
Base-centered orthorhombic |
|||
|
Rhombohedral |
Simple rhombohedral |
|
a = b = c,a = b = g ¹ 900 |
|
Hexagonal |
Simple hexagonal |
|
a = b ¹ c,
g ¹ 1200 |
|
Monoclinic |
Simple monoclinic
|
|
a ¹ b ¹ c,a = g = 900 ¹ b |
|
Base-centered monoclinic |
|||
|
Triclinic |
Simple triclinic |
|
a ¹ b ¹ c,a ¹ b ¹ g ¹ 900 |
![]()
Created by Dr. Wang